
This encounter left the man marked by the burns, including his melted gloves.

This encounter left the man marked by the burns, including his melted gloves.
No matter what you believe about the nature of "flying saucers," there is one sighting labeled the "most convincing" UFO encounter in history. According to CBC, the Falcon Lake incident in Canada is being called the "best-documented UFO case" 50 years after the actual event.
According to the account, Stefan Michalak was in the woods when he encountered a pair of "cigar-shaped objects" nearby, changing hues while floating before taking a disc shape. Michalak started drawing what he saw, which made their way online years later, before trying to get closer to the object.
"He couldn't make out any words, or anything, but he heard at least two beings communicating inside. He called out, offering mechanical help if they needed it," the It Gets Weird podcast recently detailed. "As soon as he touches the craft, the fingertips just start to melt, so it's so hot that it literally melts the gloves he's wearing...He's hit by this blast of air, that pushes him backward and sets his shirt and hat on fire. He's stumbling backward, getting pushed by this wave of air and gas, and trying to take this burning shirt and hat off."
The account goes on to say he showed symptoms of radiation sickness and had "severe burns" on his torso that look like a grate or Bingo card. Once released from the hospital, he returned to the locale to recover his "charred shirt, a melted glove and tools he'd left behind." He maintained his story until dying in 1999, never saying he encountered little green men either.
Wispy whorls on the moon’s surface are as lovely as they are strange. Scientists are starting to unravel their origins

For centuries, a mystery has been hiding in plain sight on the surface of the moon: bright, sinuous swirls that sprawl across thousands of square kilometers of the lunar landscape, visible through telescopes on Earth but defying explanation.
Now, at last, scientists are starting to understand them—and it turns out they’re weirder than anyone would have imagined.
These enigmatic “lunar swirls” are the result of ancient underground force fields that shield the moon from barrages of subatomic particles blasted out by the sun. Each swirl is a meandering blanket of pristine rock interlaced with darkened, radiation-zapped material.
Unlike Earth, the moon today doesn’t have a global magnetic field. It had a weak one billions of years ago, when it was still molten, but that died down quickly as the moon cooled. As rocks solidified on the surface, however, they were able to retain some of that ephemeral magnetism, creating more enduring localized regions with a somewhat stronger magnetic field. Given their ancient origin, these are called “relic” fields, and many are associated with lunar swirls.
The actual reason for this association became clear about a decade ago, when scientists published results in Nature Communications that showed that the relic fields around swirls, weak as they are, can still be strong enough to slightly deflect the solar wind impinging on the lunar surface. This wind consists of subatomic particles from the sun, and the trajectories of electrically charged particles such as electrons and protons can be changed by magnetic fields.
Where the relic fields are stronger, the particles veer off to the side, darkening the ground where they fall—and leaving curiously curlicue patterns in the more pristine magnetically shielded surface.
Bull’s blood isn’t poisonous; so why did people think it was for centuries?
As described in his Philosophical Dictionary in 1764, Voltaire conducted this peculiar experiment to dispel an equally strange, yet persistent, myth dating back to ancient times: that bull’s blood was a deadly poison.
“If a man in his folly tastes the fresh blood of a bull, he falls heavily to the ground in distress, over-mastered by pain,” the Greek physician Nicander wrote in the second century BC.
Nicander was echoing earlier Greek writers like Aristotle, who described bull’s blood as the “quickest to coagulate” of all animal bloods (a claim unsupported by modern research, which has found that the blood of cattle clots more slowly on average than that of some other animals such as pigs and sheep).
However, Ancient Greek scholars believed that bull’s blood solidified rapidly in the throat when swallowed, causing fatal asphyxiation. “The blood congeals easily,” Nicander explained, “and, in the hollow of [the victim’s] stomach, clots; the passages are stopped, the breath is straitened within his clogged throat, while, often struggling in convulsions on the ground, he gasps bespattered with foam.” To treat this gruesome condition,
Nicander recommended several remedies, of which some (fresh figs in vinegar) sound easier to obtain than others (the milk of a hare or deer).
You don't get more hardcore than the lammergeier.

Vultures are not always the most visually appealing birds. But bearded vultures, or lammergeiers, are beautifully done up, with glossy dark wings, long thin goatees, and KISS-worthy eye masks. Their chests, heads, and legs are especially impressive, colored the rich red brown of polished mahogany. They deserve much of the credit for their fashion sense. These vultures turn their feathers red on purpose, covering themselves in iron oxide by bathing in rusty water or rubbing themselves with damp red soil.
They are the only birds known to intentionally color themselves, and exactly why they do is still not entirely settled.
Lammergeiers eat almost exclusively bones—the last remnants of the meals of other scavengers. Bones from anything smaller than a sheep they can eat whole. They’ll fly larger ones high into the air and drop them onto rocks over and over again until they break up into swallowable pieces.
Robert Smith is convinced the aliens have won. "The invasion has happened—it's all over," says the University of Alberta space historian who teaches a course on the history of extraterrestrials.

Smith contends aliens have been invading our imagination at least since the ancients. The Greek philosopher Epicurus—who first came up with the idea that the universe is made up of atoms—speculated about other worlds, as did the Roman poet Lucretius.
In the second century CE, Lucian of Samosata wrote what is considered the first work of science fiction, a satire called "A True Story" about inhabitants of the sun and the moon fighting over the colonization of Venus.
Wells' novel was widely seen as a reflection of anxiety over British imperialism. The author once said the story was prompted by a discussion with his brother about the brutal British colonization of Tasmania; he wondered what would happen if Martians treated England the same way.
After taking the long view, does Smith believe in the existence of extraterrestrials? He prefers to defer to the great science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke. "Two possibilities exist: Either we are alone in the universe or we are not. Both are equally terrifying."
THIS fighter pilot had a real-life Independence Day moment when he emptied enough 30mm shells into a UFO to “obliterate” it.
After takeoff, Colonel Huerta flew to 2,500 metres and came in for an attack run. “I reached the necessary distance and shot a burst of sixty-four 30mm shells, which created a cone-shaped ‘wall of fire’ that would normally obliterate anything in its path,” he writes.
Just one of those shells would wipe out a car, but they had no effect on the object. “I thought that the balloon would then be torn open and gases would start pouring out of it. But nothing happened. It seemed as if the huge bullets were absorbed by the balloon, and it wasn’t damaged at all.”
The object then shot rapidly skywards away from the base, prompting Colonel Huerta to activate the plane’s afterburner to give chase 500m behind. As they reached the city of Camana, 84km from the base, the object came to a sudden stop, forcing him to veer to the side.
Turning up and to the right, Colonel Huerta attempted to position himself for another shot.
“I began closing in on it until I had it in perfect sight,” he writes. “I locked on the target and was ready to shoot. But just at that moment, the object made another fast climb, evading the attack. I was left underneath it; it ‘broke the attack’.”
He attempted the same manoeuvre two more times, and each time the object escaped by shooting upwards seconds before he could fire.
By this time the object was 14,000 metres above ground. Colonel Huerta decided to attempt an attack from above, so it could not leave his target range, but the object shadowed him all the way up to 19,200 metres — well above his aircraft’s specifications.
Running low on fuel, he realised he couldn’t continue the attack, so decided to fly close to the object to get a better look. It wasn’t until he was 100m away that he realised what it was.
“I was startled to see that the ‘balloon’ was not a balloon at all. It was an object that measured about 10 metres in diameter with a shiny dome on top that was cream-coloured, similar to a light bulb cut in half,” he writes.
“The bottom was a wider circular base, a silver colour, and looked like some kind of metal. It lacked all the typical components of aircraft. It had no wings, propulsion jets, exhausts, windows, antennae, and so forth. It had no visible propulsion system.
“At that moment, I realised this was not a spying device but a UFO, something totally unknown. I was almost out of fuel, so I couldn’t attack or manoeuvre my plane, or make a high-speed escape. Suddenly, I was afraid. I thought I might be finished.”
Colonel Huerta made his return, gliding part way due to lack of fuel and “zigzagging to make my plane harder to hit, always with my eyes on the rearview mirrors, hoping it wouldn’t chase me”.
Here is the story of Felix Moncla and Robert Wilson disappeared while intercepting an unidentified aircraft over Lake Superior, America in 1953.

During a a stormy evening on 23 November, 1953, the two men were stationed at Kinross Base (now known as Kincheloe Air Force Base) in Wisconsin when a report came in of an unidentified flying object (UFO, now known as UAP) over Lake Superior, near the commercial Soo Locks region at the US-Canadian border.
Moncla and Wilson were swiftly dispatched to perform an air defence intercept. However the pair would never return from the mission.
The pair were assisted to the unidentified object by ground radars, who watched as the two blips on the screen collided with each other and all communications and tracking with Moncla and Wilson's aircraft ceased.
The unidentified aircraft would then veer off the radar as well.
The first time Earth’s geologic record – information found inside rocks – has been used to create an animation of this kind.

Using information from inside the rocks on Earth’s surface, we have reconstructed the plate tectonics of the planet over the last 1.8 billion years.
It is the first time Earth’s geological record has been used like this, looking so far back in time. This has enabled us to make an attempt at mapping the planet over the last 40% of its history, which you can see in the animation below.
New evidence suggests that billions of years ago, a star may have passed very close to our solar system. As a result, thousands of smaller celestial bodies in the outer solar system outside Neptune's orbit were deflected into highly inclined trajectories around the sun. It is possible that some of t...
New evidence suggests that billions of years ago, a star may have passed very close to our solar system. As a result, thousands of smaller celestial bodies in the outer solar system outside Neptune's orbit were deflected into highly inclined trajectories around the sun. It is possible that some of them were captured by the planets Jupiter and Saturn as moons.
Trajectory of the stellar flyby that shaped the outer Solar System
Typically, electrons are free agents that can move through most metals in any direction. When they encounter an obstacle, the charged particles experience friction and scatter randomly like colliding billiard balls.
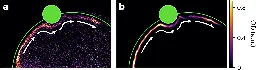
"There is no friction. There is no slowing down, and no atoms leaking or scattering into the rest of the system. There is just beautiful, coherent flow."
"These atoms are flowing, free of friction, for hundreds of microns," Fletcher adds. "To flow that long, without any scattering, is a type of physics you don't normally see in ultracold atom systems."
This effortless flow held up even when the researchers placed an obstacle in the atoms' path, like a speed bump, in the form of a point of light, which they shone along the edge of the original laser ring. Even as they came upon this new obstacle, the atoms didn't slow their flow or scatter away, but instead glided right past without feeling friction as they normally would.
Starliner is scheduled to undock from the ISS at 6:04 p.m. ET today (Sept. 6) and land six hours later.

Boeing's Starliner capsule will depart the International Space Station without astronauts today (Sept. 6), and you can watch the action live.
A livestream of Starliner's homecoming will begin at 5:45 p.m. EDT (2145 GMT) today, featuring the capsule's undocking at 6:04 p.m. EDT (2204 GMT). You can watch it here at Space.com, via NASA Television.
Reddit’s crisis is a warning for all social platforms: when you trade community for profits, everyone loses. Will Reddit fix its mes...

Money, Mods, and Mayhem
The Turning Point
In 2024, Reddit is a far cry from its scrappy startup roots. With over 430 million monthly active users and more than 100,000 active communities, it's a social media giant. But with great power comes great responsibility, and Reddit is learning this lesson the hard way.
The turning point came in June 2023 when Reddit announced changes to its API pricing. For the uninitiated, API stands for Application Programming Interface, and it's basically the secret sauce that allows third-party apps to interact with Reddit. The new pricing model threatened to kill off popular third-party apps like Apollo, whose developer Christian Selig didn't mince words: "Reddit's API changes are not just unfair, they're unsustainable for third-party apps."
Over 8,000 subreddits went dark in protest.
The blackout should have reminded Reddit’s overlords of a crucial fact: Reddit’s success was built on the backs of its users. The platform had cultivated a sense of ownership among its community, and now that community was biting back.
One moderator summed it up perfectly: “We’re the ones who keep this site running, and we’re being ignored.”
The Roman siege system of Masada: a 3D computerized analysis of a conflict landscape
Our analysis, based on a thorough survey, ground-level recording, and a digital photogrammetric 3D model, shows that the construction of both the wall and the camps around Masada took about two weeks. This supports Roth's argument for a four-to-nine-week siege.
The circumvallation was also built as a means of psychological warfare against the besieged. In fact, the sections above the south and west cliffs were built only to lower the defenders’ morale and to function as a symbol of Roman might.
The audience for the psychological warfare may also have been the Roman soldiers themselves – Levithan showed that the Roman legions besieging Jerusalem only a few years prior were not an unstoppable war-machine; in fact, their commanders did not have full control over them, as soldiers avoided dangerous circumstances and officers had to persuade them to volunteer for more dangerous missions.
The impressive circumvallation around Masada probably helped the Roman army's morale by boosting soldier confidence – an important factor in ancient warfare.
Mars was once a very wet planet as is evident in its surface geological features. Scientists know that over the last 3 billion years, at least some water went deep underground, but what happened to the rest? Now, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) missio...

Mars was once a very wet planet as is evident in its surface geological features. Scientists know that over the last 3 billion years, at least some water went deep underground, but what happened to the rest? Now, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) missions are helping unlock that mystery.
"There are only two places water can go. It can freeze into the ground, or the water molecule can break into atoms, and the atoms can escape from the top of the atmosphere into space."
The whole atmosphere is very turbulent, heating up and cooling down on short timescales, even down to hours. The atmosphere expands and contracts as the brightness of the Sun at Mars varies by 40 percent over the course of a Martian year.
The team discovered that the escape rates of hydrogen and deuterium change rapidly when Mars is close to the Sun. In the classical picture that scientists previously had, these atoms were thought to slowly diffuse upward through the atmosphere to a height where they could escape.
But that picture no longer accurately reflects the whole story, because now scientists know that atmospheric conditions change very quickly. When Mars is close to the Sun, the water molecules, which are the source of the hydrogen and deuterium, rise through the atmosphere very rapidly releasing atoms at high altitudes.
The second finding is that the changes in hydrogen and deuterium are so rapid that the atomic escape needs added energy to explain them. At the temperature of the upper atmosphere only a small fraction of the atoms have enough speed to escape the gravity of Mars. Faster (super-thermal) atoms are produced when something gives the atom a kick of extra energy. These events include collisions from solar wind protons entering the atmosphere or sunlight that drives chemical reactions in the upper atmosphere.
Our solar system has eight planets, and five dwarf planets - all located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy called the Orion Arm.
Planets
The solar system has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. There are five officially recognized dwarf planets in our solar system: Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris.
Inner Planets
The first four planets from the Sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These inner planets also are known as terrestrial planets because they have solid surfaces.
Outer Planets
The giant planets in our outer solar system don't have hard surfaces and instead have swirling gases above a core. Jupiter and Saturn are gas giants. Uranus and Neptune are ice giants.
Dwarf Planets
Beyond Neptune, a newer class of smaller worlds called dwarf planets reign, including longtime favorite Pluto. The other dwarf planets are Ceres, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris. Ceres is the only dwarf planet in the inner solar system. It's located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
A spacecraft carrying European and Japanese probes passed closer to Mercury than originally planned overnight after thruster problems delayed the mission to study the little-known, sun-scorched planet.

A spacecraft carrying European and Japanese probes passed closer to Mercury than originally planned overnight after thruster problems delayed the mission to study the little-known, sun-scorched planet.
The new path meant the spacecraft needed to fly 35 kilometers (22 miles) closer to the planet than initially planned—passing just 165 kilometers above the surface—during its latest flyby.
The European Space Agency's operations team confirmed that "all went well" with the flyby overnight. It also posted a new image taken by the probe of the planet, whose pockmarked surface resembles the moon.
Mercury is by far the least studied of the four rocky, innermost planets in our solar system, which also include Venus, Earth and Mars.
The quest to find life beyond Earth has long been a topic of fascination for scientists, scholars, and the general public alike. Central to this pursuit is the concept of “habitability,”…

Traditional Views on Habitability: The Goldilocks Zone
Traditionally, the search for habitable environments beyond Earth has centered around the concept of the “Goldilocks Zone” or the “Habitable Zone.” This is the region around a star where conditions are just right—neither too hot nor too cold—for liquid water to exist on a planet’s surface. The presence of liquid water has been considered a critical factor for life as we know it, mainly due to its role as a universal solvent in biochemical processes. This notion has shaped many astronomical surveys and planetary missions, focusing on planets that reside within this special zone around their host stars.
Expanding the Parameters: Extremophiles and Alternative Solvents
Recent discoveries in the field of astrobiology have begun to challenge and expand our understanding of habitability. Organisms known as “extremophiles” have been found in extreme conditions on Earth, such as in acidic lakes, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and even in the radiation-rich environments of nuclear reactors. These findings suggest that life can exist in a wider range of conditions than previously thought, leading scientists to consider other factors beyond the presence of liquid water.
Additionally, there is growing interest in the potential for life to exist in environments with solvents other than water. For example, the methane lakes on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, present an interesting case for astrobiologists. While methane is not as versatile a solvent as water, it could theoretically support some forms of life, broadening the scope of what scientists consider “habitable.”
Survey observations using the Subaru Telescope's ultra-widefield prime focus camera have revealed that there may be a population of small bodies further out in the Kuiper Belt waiting to be discovered.
Survey observations using the Subaru Telescope's ultra-widefield prime focus camera have revealed that there may be a population of small bodies further out in the Kuiper Belt waiting to be discovered.
There have been five spacecraft that have flown to the outer solar system (including New Horizons), but New Horizons is the only spacecraft that has flown through the Kuiper Belt while observing Kuiper Belt objects.
Societal collapse is a complex phenomemon tied to the abilities of a society to meet its population’s basic needs. Understanding past examples of collapse can provide valuable insights.

Researchers often define collapse as a social simplification in which hierarchies are flattened or governance systems break up. But with this definition it’s not clear what is inherently “bad” about collapse. After all, the disintegration of colonial empires in the mid-20th century was a collapse by this definition — and a development which most would celebrate.
We argue that the demise of a social hierarchy need not entail societal collapse, what matters is how events impact human welfare. Therefore, it is necessary to pin down what exactly is harmful about collapse before trying to generalize from past examples. After all, the purpose of learning from history should be to prevent wrongs, not protect contemporary inequalities.
Bright lights at night may alter the brains of nocturnal arachnids, our new study shows. And we’re only just learning what this means for our ecosystems.

In new research published in Biology Letters, we studied how light pollution affects the development of Australian garden orb weaving spiders. We discovered it makes their brains smaller, particularly in the regions devoted to vision – with unknown effects on their behaviour.
What light pollution means for animals
Artificial light is one of the fastest-growing ways humans are polluting the world, and it has a huge range of effects on animals, plants and ecosystems. Recent evidence suggests the stress of living with light pollution may impair the growth and development of the brain in some birds and mammals.
This may be catastrophic. To survive in novel environments where light pollution is most common, such as cities, animals may actually need larger and more complex brains.
But what about insects and spiders and other, smaller creatures that inhabit the night? Could light pollution similarly affect the growth and development of their brains?
Our study on the nocturnal Australian garden orb weaving spider suggests it does.
